ClassLoader即java类加载机制
java依赖于JVM实现的跨平台编译型语言,ClassLoaer其实是一个组件,用于将java源码编译成的class文件加载进JVM
具体流程:
// TODO
拥有多个加载器各司其职,BootstrapClassLoader(引导类加载器)、ExtensionClassLoader(扩展类加载器)、AppClassLoader(系统类加载器),(高版本是BootstrapClassLoader、PlatformClassLoader、AppClassLoader)我们编写的Java默认使用AppClassLoader加载
加载器之间可以通过getParent()获取父加载器,本质上通过加载器内定义的parent常量指向父加载器,非继承
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
public final ClassLoader getParent() {
if (parent == null)
return null;
@SuppressWarnings("removal")
SecurityManager sm = System.getSecurityManager();
if (sm != null) {
// Check access to the parent class loader
// If the caller's class loader is same as this class loader,
// permission check is performed.
checkClassLoaderPermission(parent, Reflection.getCallerClass());
}
return parent;
}
|
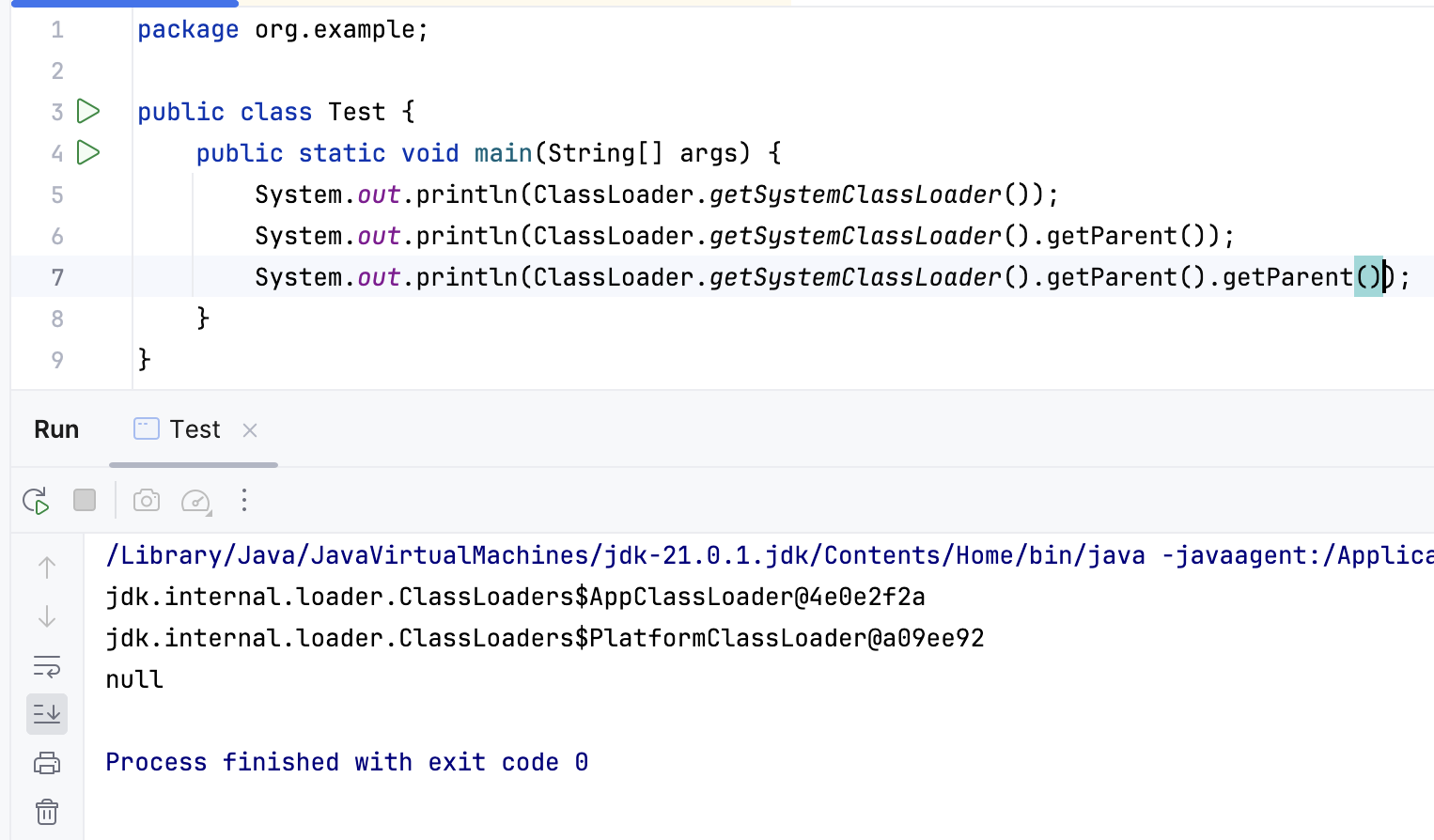
BootstrapClassLoader实现在JVM中,采用C++编写,因此尝试获取被BootstrapClassLoader加载器加载的类的ClassLoader都返回null
双亲委派
类的加载是一个递归的过程,类加载器查找class过程首先判断这个类是否已经加载成功,如果没有,则进入父加载器(只看缓存不查找),一直向上,直到BootstrapClassLoader,然后在BootstrapClassloader中执行查找操作,如果没找到则返回上一级进行查找操作,最终返回到自身去执行查找
ClassLoader的几个重要方法
loadClass():用于加载类,执行findLoadedClass(String)去检测class是否被加载,然后再执行父类的loadClass,如果parent为null,则使用JVM内置加载器去加载,loadClass很好的解释了双亲委派
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
|
protected Class<?> loadClass(String name, boolean resolve)
throws ClassNotFoundException
{
synchronized (getClassLoadingLock(name)) {
// First, check if the class has already been loaded
Class<?> c = findLoadedClass(name);
if (c == null) {
long t0 = System.nanoTime();
try {
if (parent != null) {
c = parent.loadClass(name, false);
} else {
c = findBootstrapClassOrNull(name);
}
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
// ClassNotFoundException thrown if class not found
// from the non-null parent class loader
}
if (c == null) {
// If still not found, then invoke findClass in order
// to find the class.
long t1 = System.nanoTime();
c = findClass(name);
// this is the defining class loader; record the stats
PerfCounter.getParentDelegationTime().addTime(t1 - t0);
PerfCounter.getFindClassTime().addElapsedTimeFrom(t1);
PerfCounter.getFindClasses().increment();
}
}
if (resolve) {
resolveClass(c);
}
return c;
}
}
|
findLoadedClass():很好理解,调用findeLoadedClass0方法,它是一个native方法
1
2
3
4
5
|
protected final Class<?> findLoadedClass(String name) {
if (!checkName(name))
return null;
return findLoadedClass0(name);
}
|
findClass():根据名称和位置读取字节码,并调用defineClass方法,需要子类去实现
defineClass():将byte数组形式的字节码转换成对应的Class对象,这里是加载字节码的位置
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
protected final Class<?> defineClass(String name, byte[] b, int off, int len,
ProtectionDomain protectionDomain)
throws ClassFormatError
{
protectionDomain = preDefineClass(name, protectionDomain);
String source = defineClassSourceLocation(protectionDomain);
Class<?> c = defineClass1(this, name, b, off, len, protectionDomain, source);
postDefineClass(c, protectionDomain);
return c;
}
|
自定义ClassLoader
可以自己重写findClass来自定义ClassLoader根据自己的需求去加载class
这边做了一个加载指定目录下的制定class文件,并且判断class的名字是不是Test,如果不是就用其他ClassLoader加载
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
|
package org.example;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.nio.file.Files;
import java.nio.file.Path;
import java.nio.file.Paths;
public class TestClassLoader extends ClassLoader {
@Override
public Class<?> findClass(String pathS, String name) {
try {
Path path = Paths.get(pathS , name + ".class");
byte[] bytes = Files.readAllBytes(path);
if (name.equals("Test")) {
return defineClass(name, bytes, 0, bytes.length);
}
return super.findClass(name);
} catch (IOException | ClassNotFoundException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
TestClassLoader loader = new TestClassLoader();
Class testClass = loader.findClass(System.getProperty("user.dir"), "Test");
Constructor testConst = testClass.getConstructor();
Object test = testClass.newInstance();
Method calc = testClass.getDeclaredMethod("calc");
calc.invoke(test);
}
}
|
